[AWS SAA-C02 Study Note] Computing: EC2, ELB, AMI, ASG
EC2
Elastic Computing Cloud
Cloud Computing Service: choose your OS, storage, memory, network throughput. launch and SSH into your server within minutes.

Instance Types

Supplement: Spot Fleet
A Spot Fleet is set of Spot Instances and optionally On-Demand Instances that is launched based on criteria that you specify.
The Spot Fleet selects the Spot capacity pools that meet your needs and launches Spot Instances to meet the target capacity for the fleet.
By default, Spot Fleets are set to maintain target capacity by launching replacement instances after Spot Instances in the fleet are terminated. You can submit a Spot Fleet as a one-time request, which does not persist after the instances have been terminated. You can include On-Demand Instance requests in a Spot Fleet request.
Instance Size
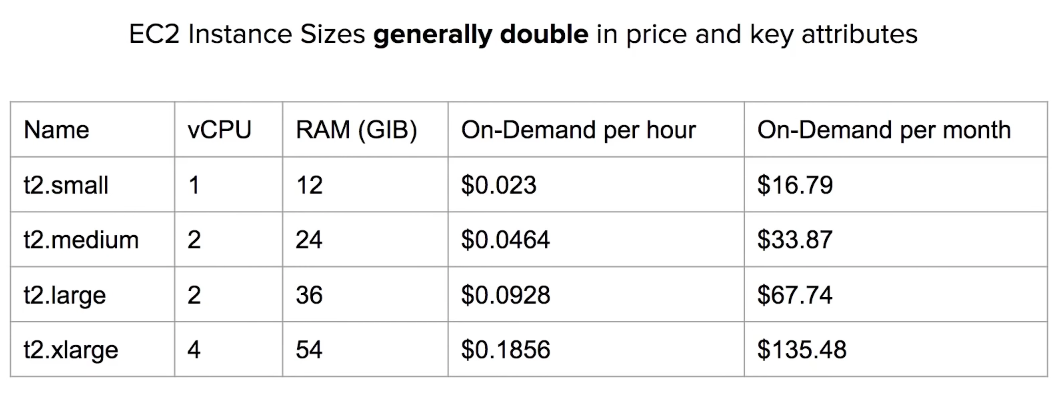
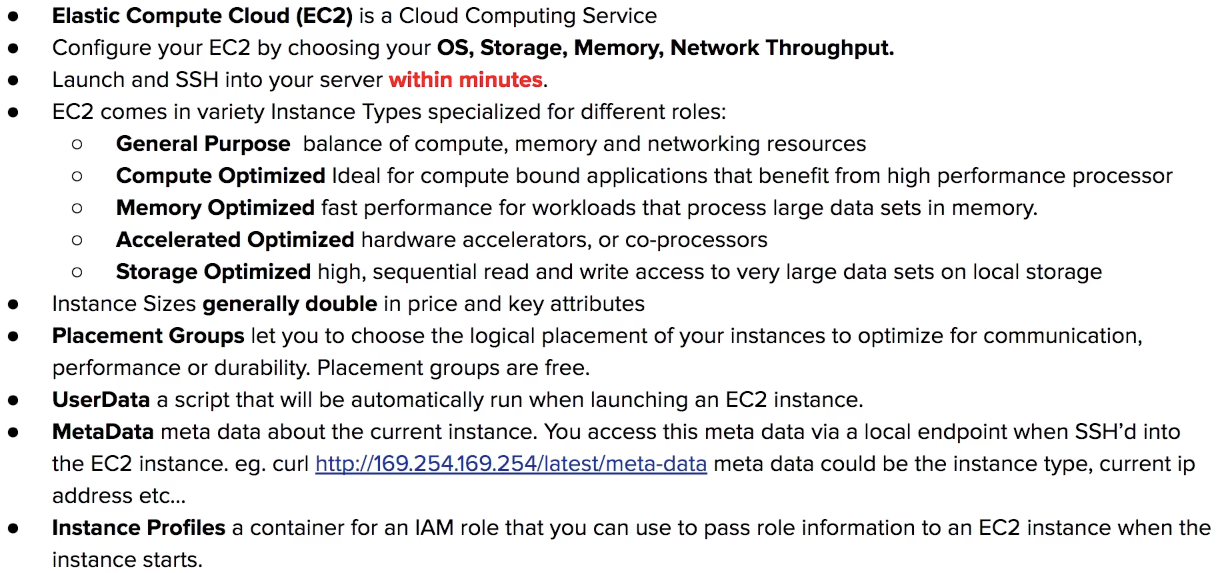
Instance Profiles
Attach a role to an instance via an Instance Profile
Always avoid embedding your AWS credentials when possible
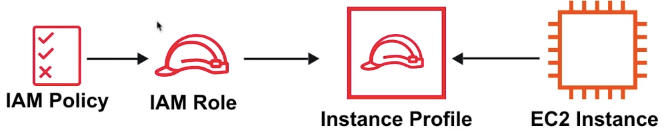
An Instance Profile holds a reference to a role. The EC2 instance is associated with the Instance Profile. When you select an IAM role when lauching an EC2 isntance, AWS will automatically creeate the Instance Profile for you.
Placement Group
PG let you choose the logical placement of your instances to optimize for communication, performance or durability.
free service

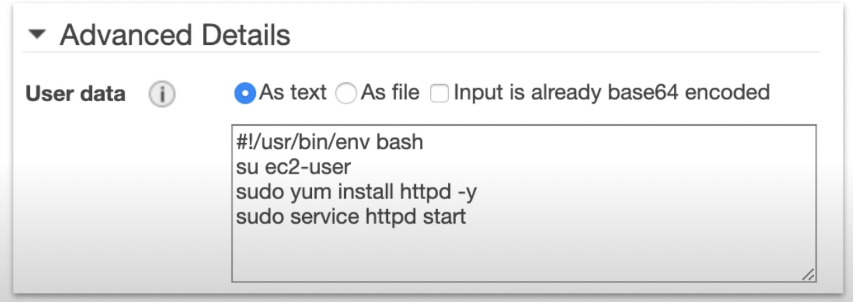
UserData
You can provide an EC2 with UserData which is a script that will automatically run when lauching an EC2 instance. You could install package, apply updates or anything you like.
Within EC2 instance, if you were to SSH in and CURL this special URL, you can see the UserData script
curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-dataMetaData
Within EC2 instance, you can access information about the EC2 via a special URL endpoint
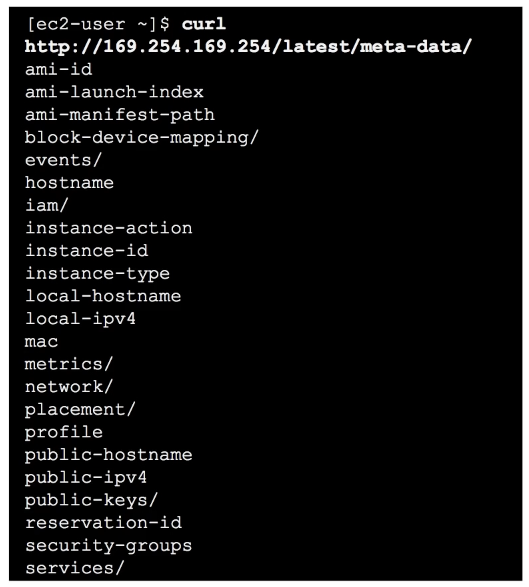
curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-ipv4 get the current public IPv4 address
/ami-id the AMI ID used to luanch this EC2 instance
/instance-type the Instace Type of this EC2 instance
EC2 Cheat Sheet
EC2 Pricing
Pricing Model
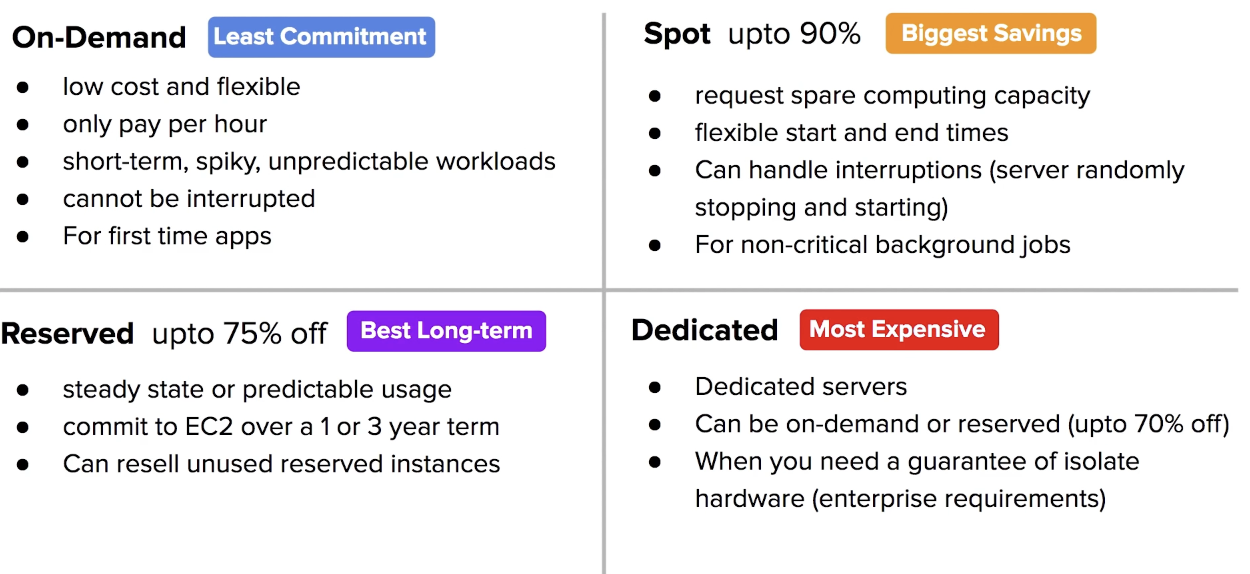
On-Demand
when you launch EC2 instance, it is default by using On-Demand Pricing
On-Demand has no up-front payment and no long-term commitment
you are charged by hour or by the minute (varies based on EC2 Instance Types)
On-Demand is for applications where the workload is for short-term, spikey or unpredictable
ex. new app for deployment
Reserved Instance
steady-state, predictable usage, or require reserved cpacity
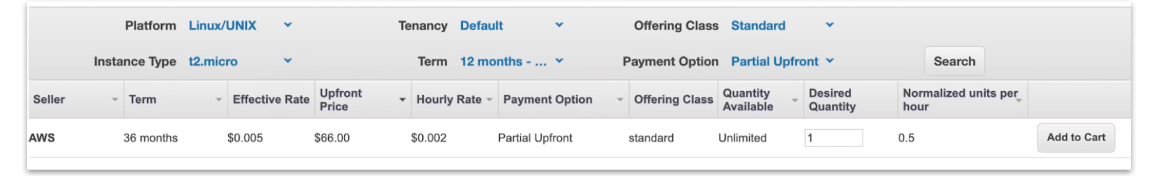
term * class offering * payment option
- Standard Up to 75% reduced pricing compared to on-demand (Cannot Change RI Attributes)
- Convertible Up to 54% reduced pricing compared to on-demand (Allows you to change RI Attributes if greater or equal in value)
- Scheduled You reserve instances for specific time periods (eg. once a week for a few hours)
Terms
commit to a 1 year or 3 year contract
Payment Options
All upfront, Partial Upfront, and No Upfront (The greater upfront the great savings)
RIs can be shared between multiple accounts within an org Unused RIs can be sold in the Reserved Instance Marketplace
EC2 Spot Instances
AWS has unused compute capcity that they want to maximize the utility of their idle servers.
Spot Instances provide a discount of 90% compared to On-Demand Pricing
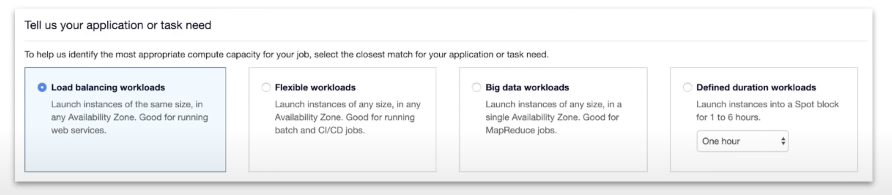
Designed for applications that have flexible start and end times or applications that are only feasible at very low compute cost
AWS Batch
an easy and convenient way to use Spot Pricing
Termination Conditions
Instances can be terminated by AWS at anytime
If ypu instance is terminated by AWS, you don’t get charged for a partial hour of usage
If you terminate an instance, you will still be charged for any hour that it ran
Dedicated Host Instances
When you have strict server-bound licensing that won’t support for multi-tenancy or cloud deployments.
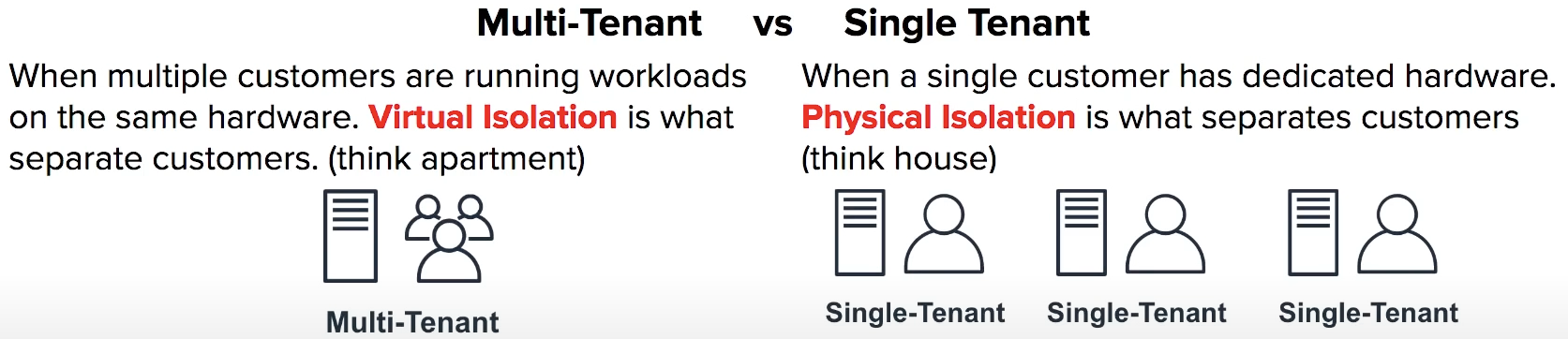
Offered in both On-Demand and Reserved (70% off on-demand pricing)

EC2 Pricing Cheat Sheet


AMI
Amazon Machine Image
provides the information required to launch an isnatnce
you can turn your EC2 instances into AMIs so you can create copies of your servers
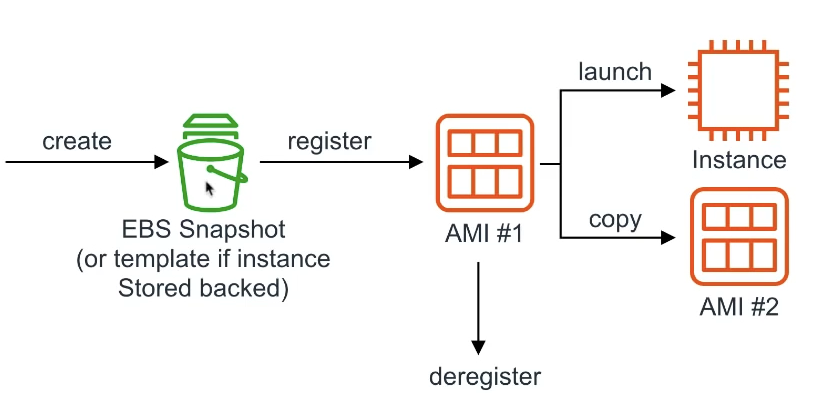
! AMI is region specific
An AMI holds following information:

AMI Use Case
AMIs help you keep incremental changes to your OS, application code and system package


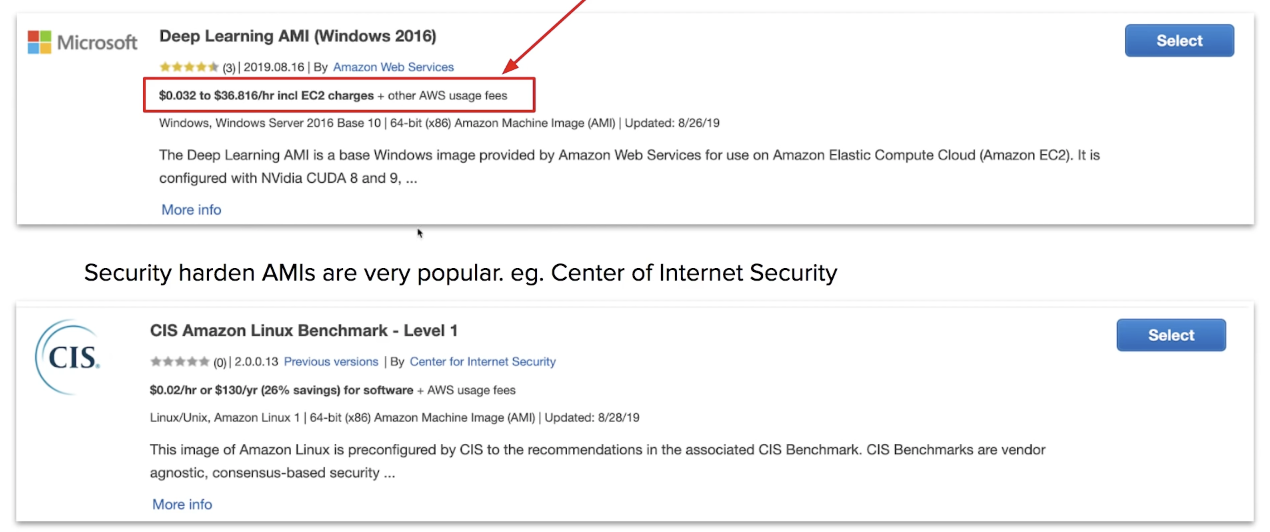
AMI Marketplace
purchased subscriptions to vendor maintained AMIs
Creating an AMI
You can create an AMI from an existing EC2 instance that’s either running or stopped.
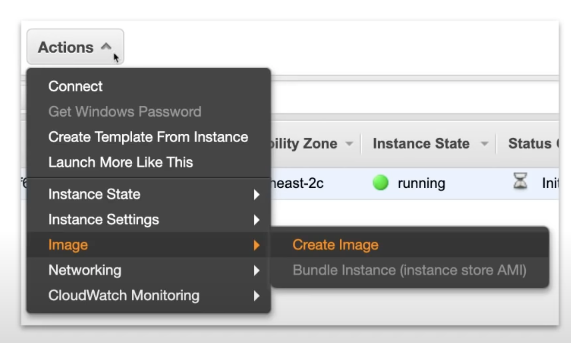
Choosing an AMI
Community AMI are free AMIs maintained by the community AWS marketplace free or paid AWS AMIs maintained by vendors
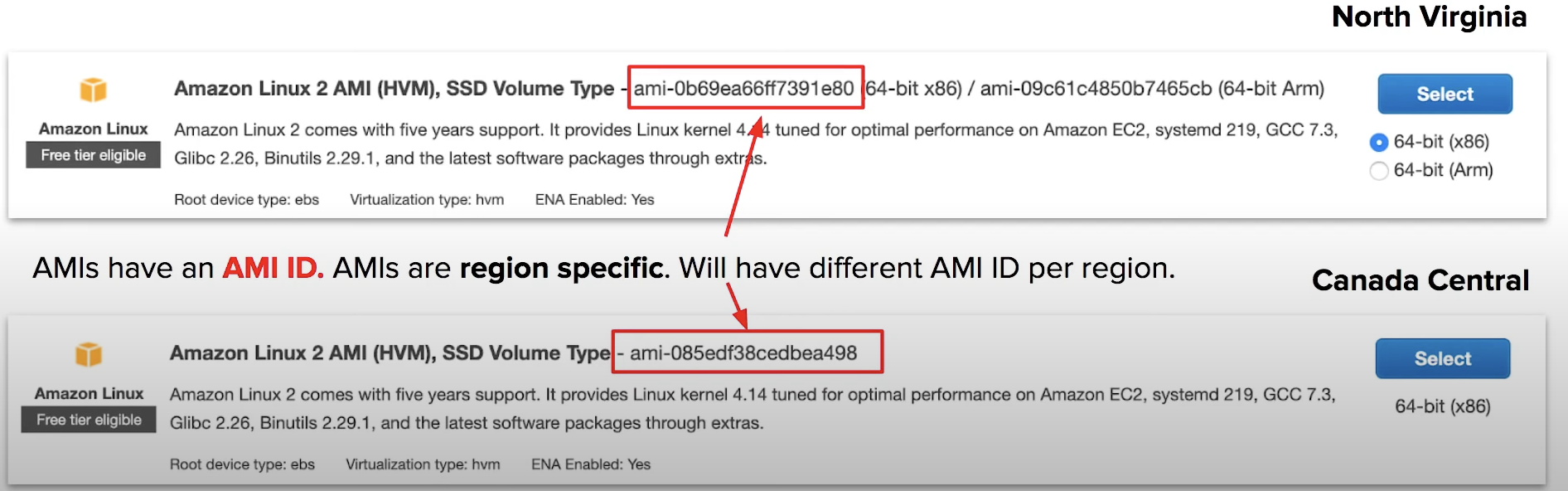
AMIs can be selected based on:
- region
- operating system
- archiecture (32bit or 64bit)
- launch permissions
- root device volume (Instance Store or EBS Backed Volumes)
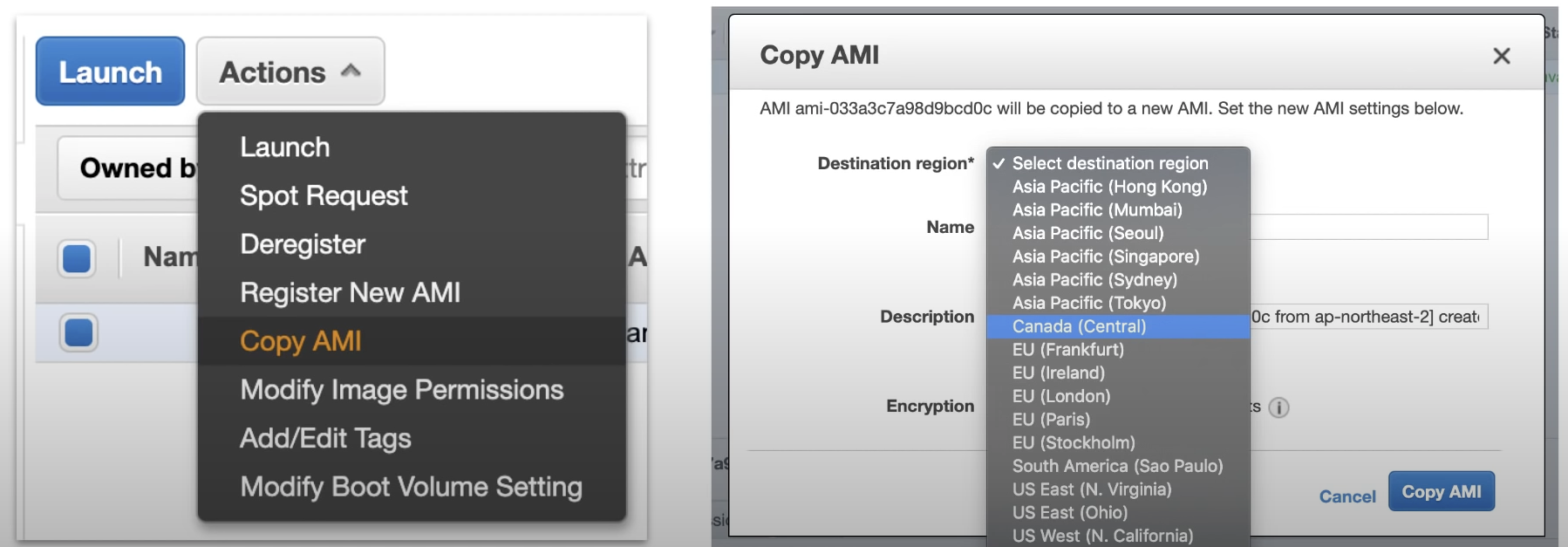
Copying an AMI
If you want to use an AMI from another region. You need to Copy the AMI and then select the destination region.
AMI Cheat Sheet

Auto Scaling Group (ASG)
set scaling rules which will automatically launch additional EC2 instance or shutdown instances to meet current demand

Automatic scaling can occur via:
- Capacity Settings
- Health Check Replacement
- Scaling Policies
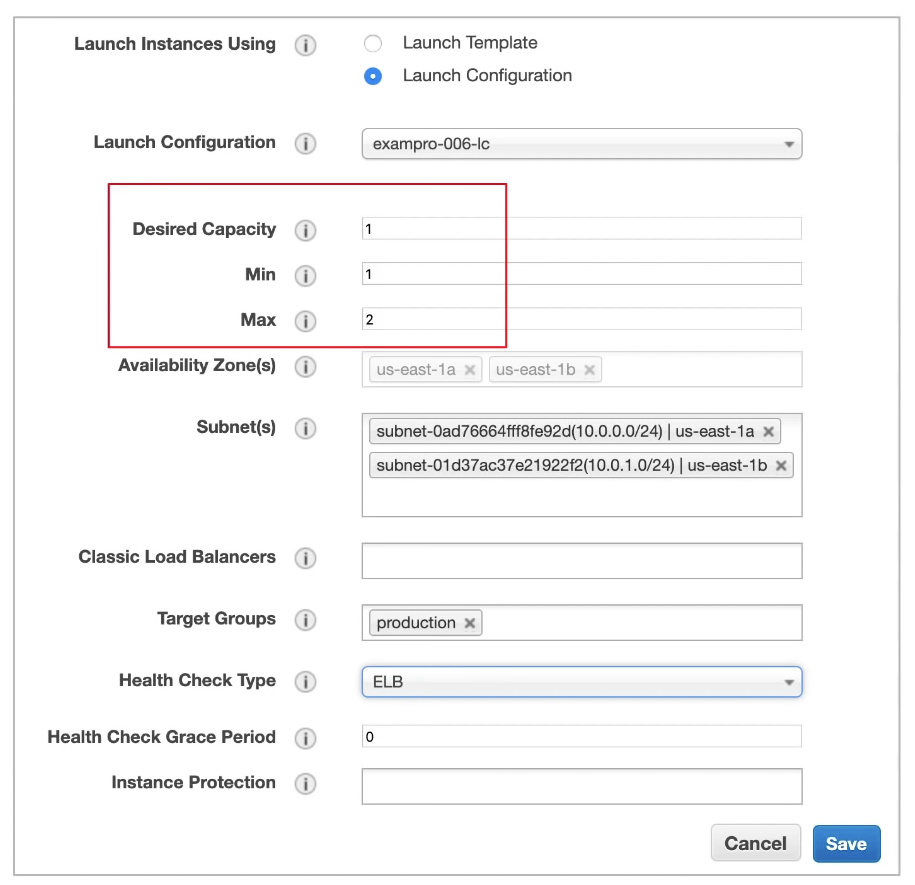
Capacity Settings
The isze of ASG is based on Min, Max and Desired Capacity
Min is how many EC2 instances should at least be running
Max is number of EC2 instances allowed to be running
Desired Capacity is how many EC2 instances you want to ideally run
ASG will always launch instances to meet minimum capacity
Health Check Replacment
two types
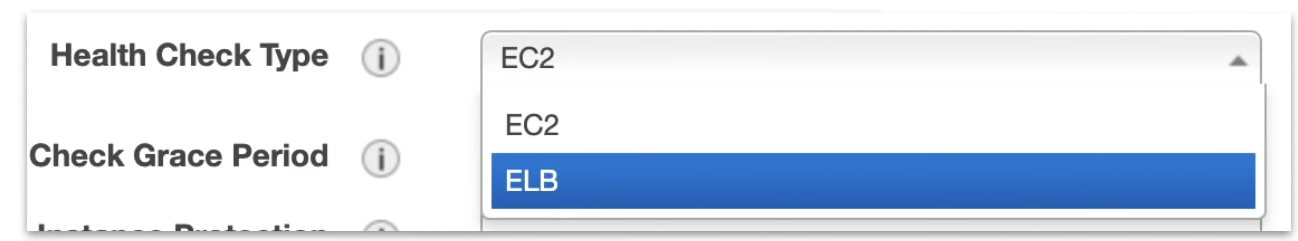
EC2 type
ASG will perform a health check on EC2 instances to determine if there is a software or hardware issue. If an instance is considered unhealthy, ASG will terminate and launch a new instance.
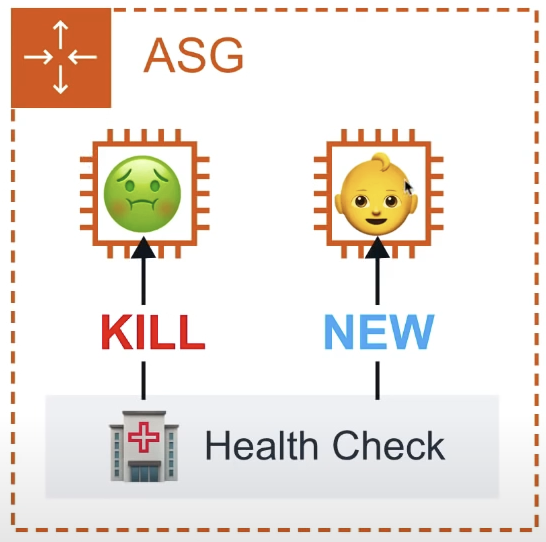
ELB type
ASG will perform a health check based on the ELB health check. ELB can perform health checks by pinging an HTTP(S) endpoint with an expected response. If ELB determines a instance is unhealthy if forwards this information to ASG whcih will terminate the unhealthy instance.
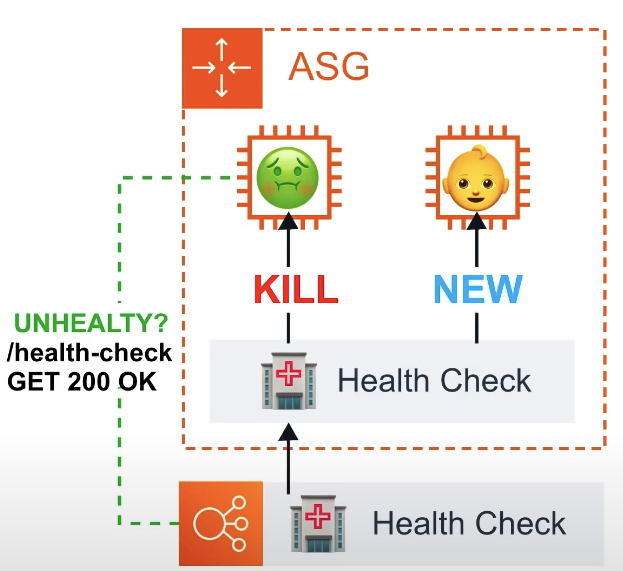
Scaling Polcies
Scaling Out: Adding More Instances
Scaling In: Removing Instances
(1) Target Tracking Scaling Policy
maintains a specific metric at a target value
ex. If Averge CPU Utilization exceeds 75%, then add another server
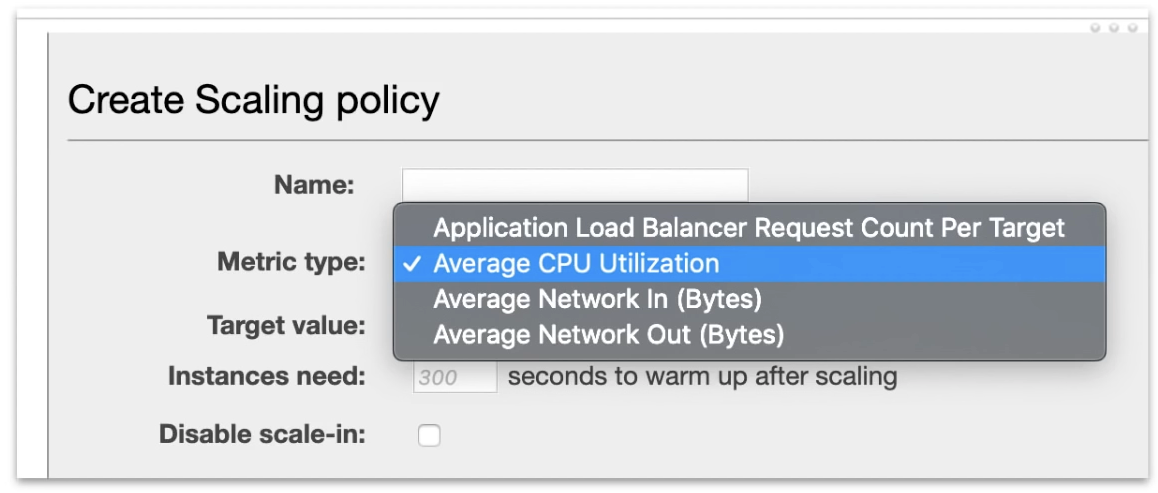
(2) Simple Scaling Policy
Scales when an alarm is breached.
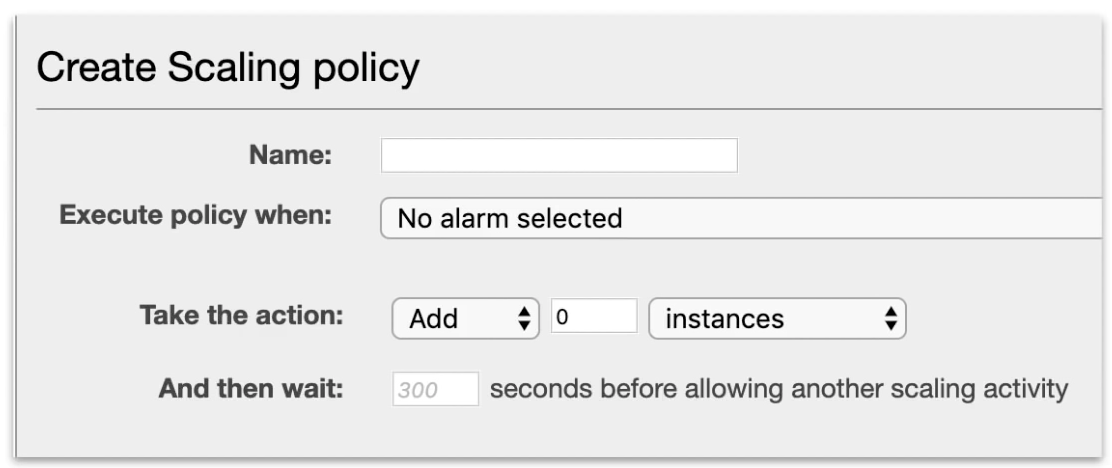
not recommended, legacy scaling policy. use scaling policies with steps now
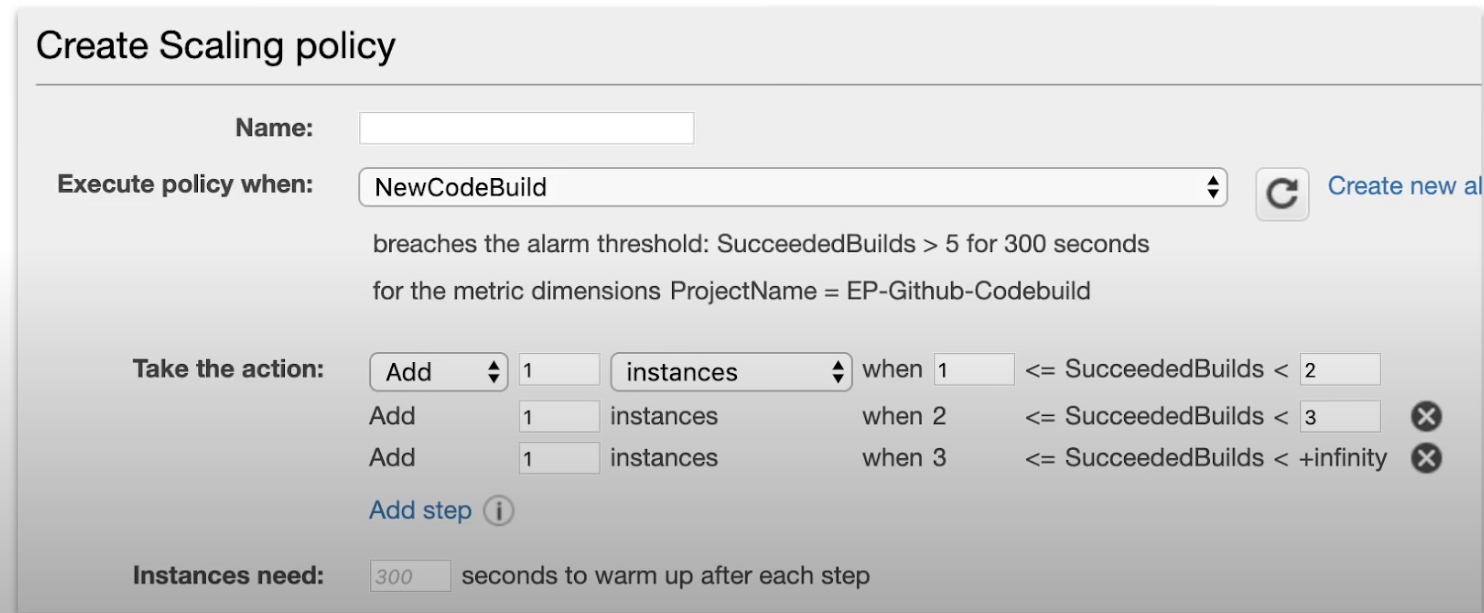
(3) Scaling Policies with Steps
Scales when an alarm is breached, can escalates based on alarm value changing
ELB Integration
ASG can be associated with ELB. When ASG is associated with ELB richer health checks can be set.

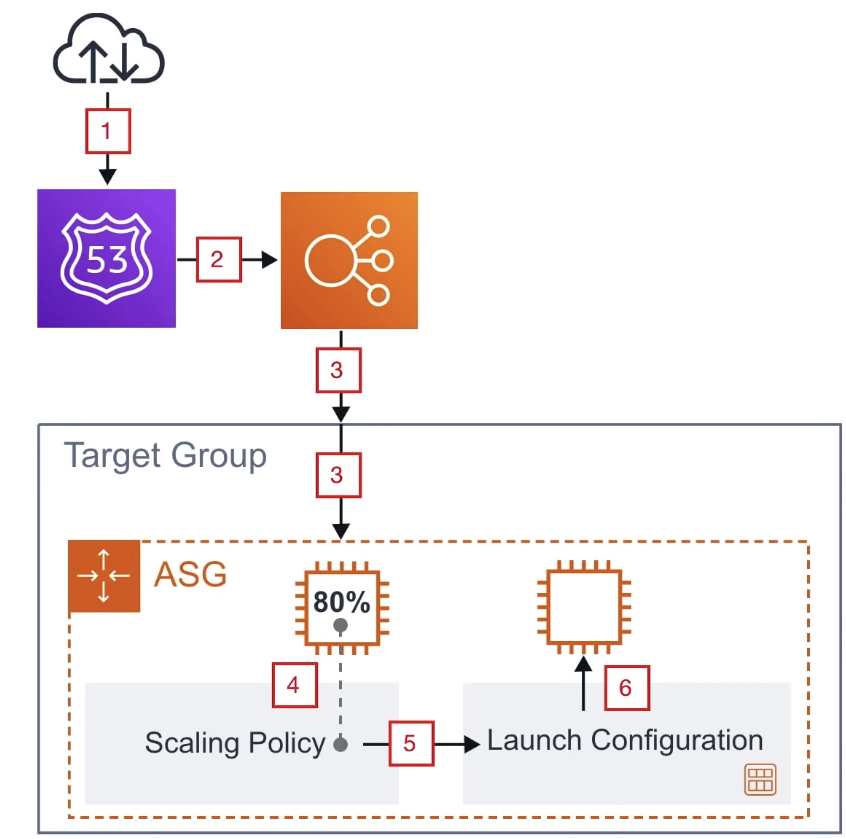
Usecase
- Burst of traffic from the Internet hits our domain.
- Route53 points that traffic to our load balancer.
- Load balancer passes the traffic to its target group.
- Target group is associated with ASG and sends the traffic to instances registered with ASG.
- The ASG Scaling Policy will check if our instances are near capcity.
- The Scaling Policy determines we need another instance, and it Launches an new EC2 instance with the associated Launch Configuration to our ASG.
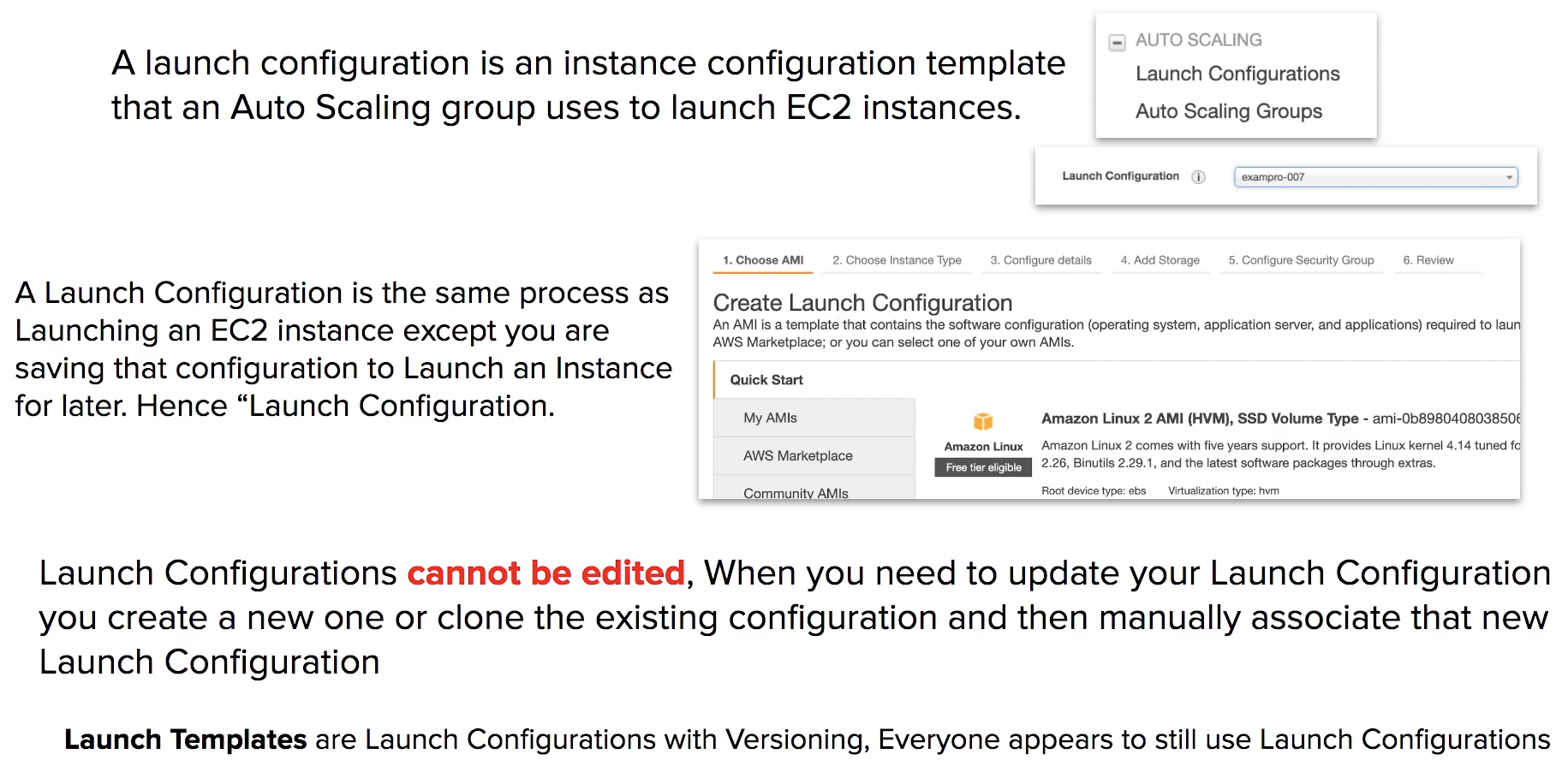
Launch Configuration
Step Scaling and Target Scaling (Scaling Policy)
Step Scaling
CloudWatch Alarm
With step scaling, you choose scaling metrics and threshold values for the CloudWatch alarms that trigger the scaling process as well as define how your scalable target should be scaled when a threshold is in breach for a specified number of evaluation periods.
ex.
When you create a step scaling policy, you add one or more step adjustments that enable you to scale based on the size of the alarm breach. Each step adjustment specifies the following:
- A lower bound for the metric value
- An upper bound for the metric value
- The amount by which to scale, based on the scaling adjustment type
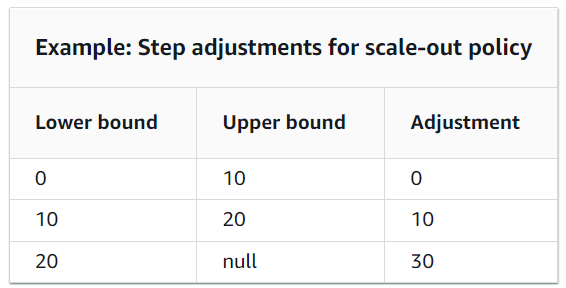
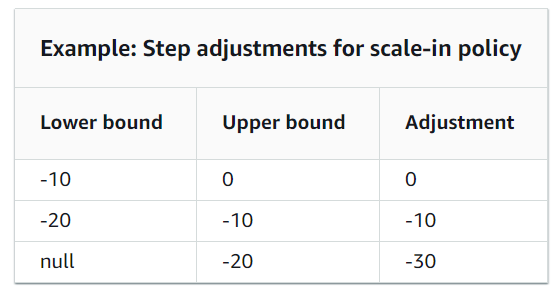
Target Scaling
Metrics on Target Value
With target tracking scaling policies, you choose a scaling metric and set a target value. Application Auto Scaling creates and manages the CloudWatch alarms that trigger the scaling policy and calculates the scaling adjustment based on the metric and the target value.
some predefined metrics on EC2 (CPU, Memory, etc)
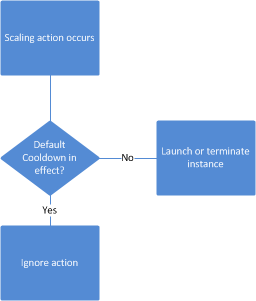
Scaling Cooldown
A scaling cooldown helps you prevent your Auto Scaling group from launching or terminating additional instances before the effects of previous activities are visible.
Ex. cooldown period = 7 minute
the first instance is launched after 3 minutes, the second instance is launched after 4 minutes, how many minutes after the first instance is launched will ASG accept another scaling acitivity
1st → 3+7
2nd → 4+7
Thus, new activity after 11 minutes
ASG Cheat Sheet

ELB
Elastic Load Banlancer
Distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, IP addresses, and Lambda functions.

The Rules of Traffic

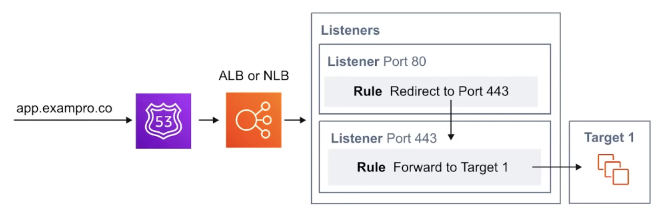
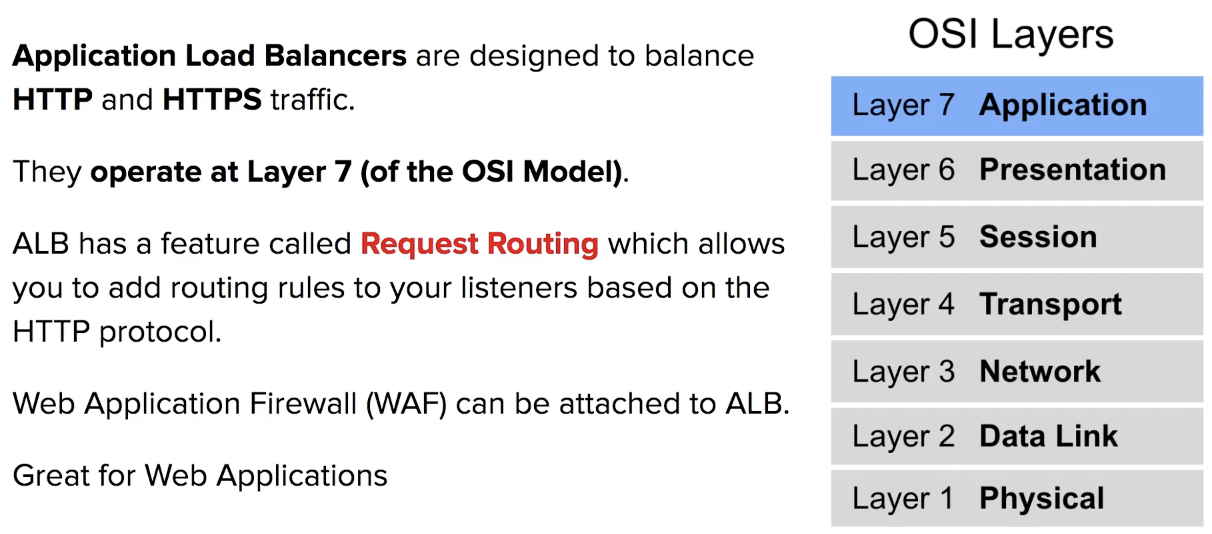
Application Load Balancer (ALB) and Network Load Balancer (NLB)
traffic is sent to the Listeners when the port matches it then checks the rules what to do.
The rules will forward the traffic to target group and target group will finally distribute the traffic to instances registered to that target group.
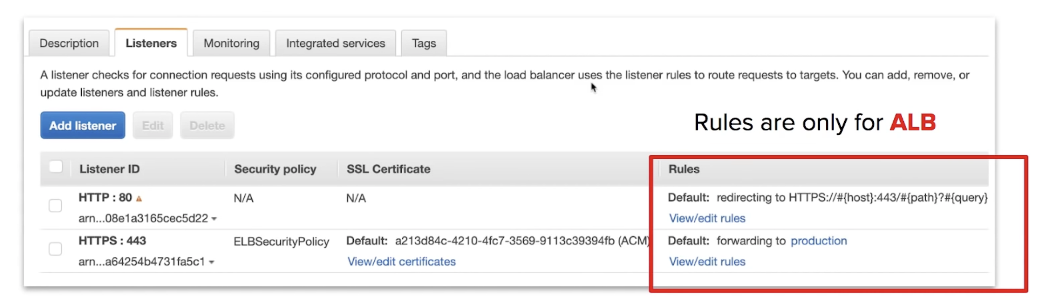
Classical Load Balancer (CLB)
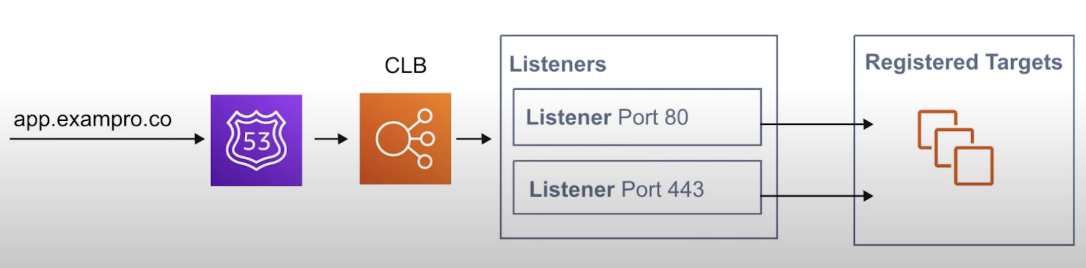
traffic is sent to Listeners. When the port matches it then it forwards the traffic to any EC2 instances that are registered to CLB. CLB does not allow you to apply any rules to listeners.
ALB
NLB

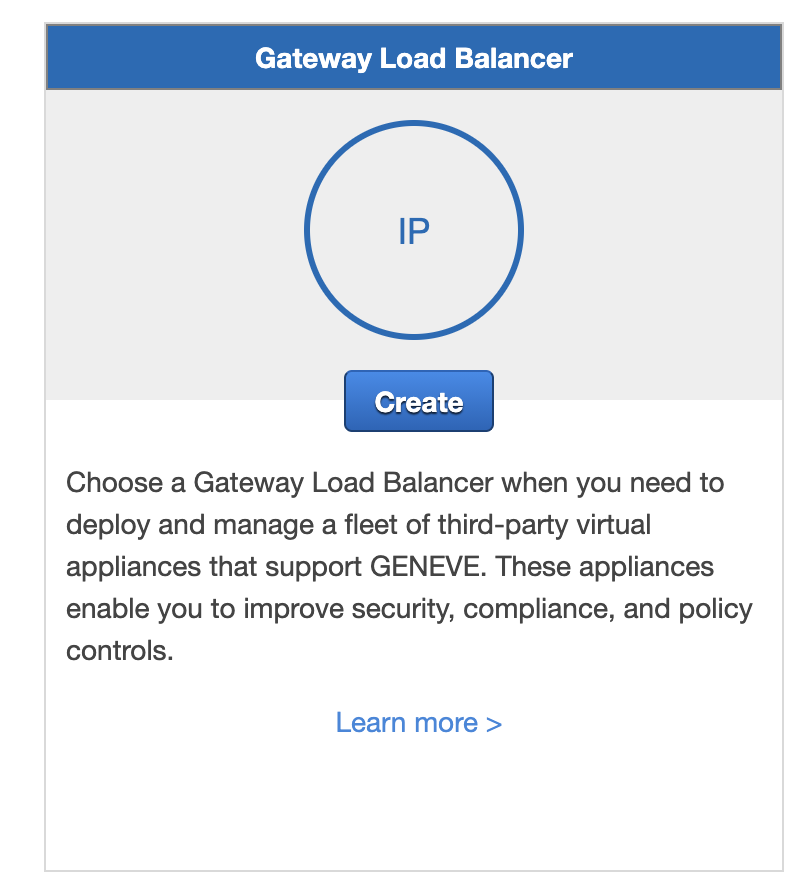
GLB
Gateway Load Balancer for IP
CLB
Sticky Session
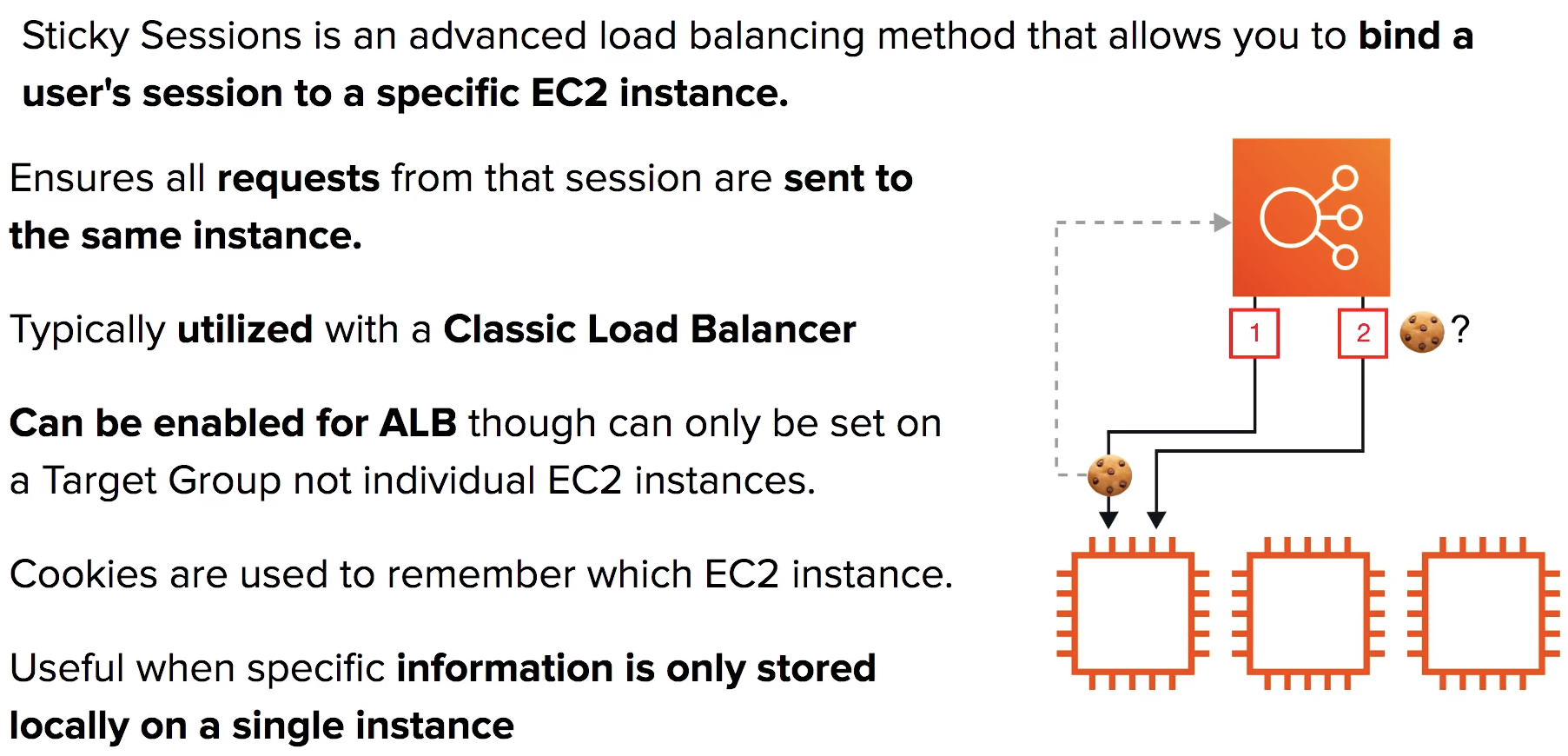
mainly for cookie
X-Forward-For (XFF) Header
If you need IPv4 address of a user, check the XFF header
XFF header is a command method for identifying the originating IP address. of a client connecting to a web server through an HTTP proxy or a load balancer.
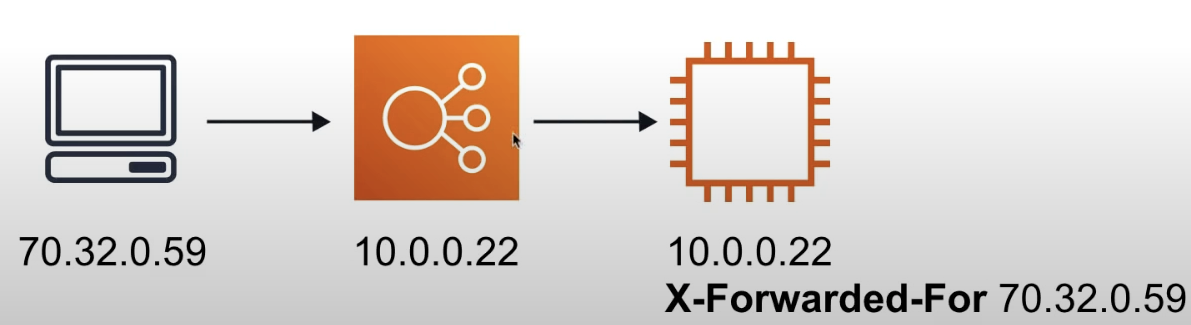
standard header
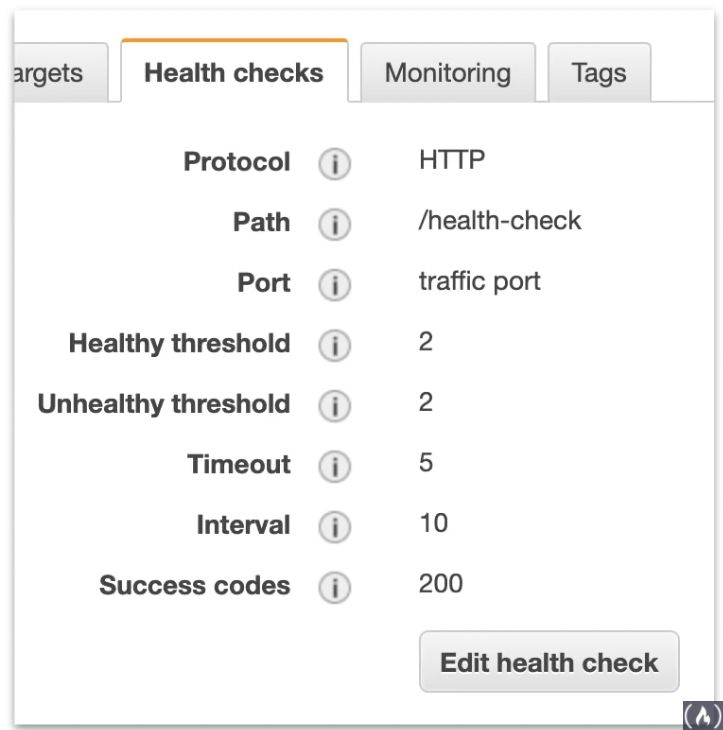
Health Checks
Instances are monitored by the ELB report back Health Checks as InService, OutofService
HC communicate directly with the instance to determine its state
ELB does not terminate (kill) unhealthy instance. It will just redirect traffic to healthy instances.
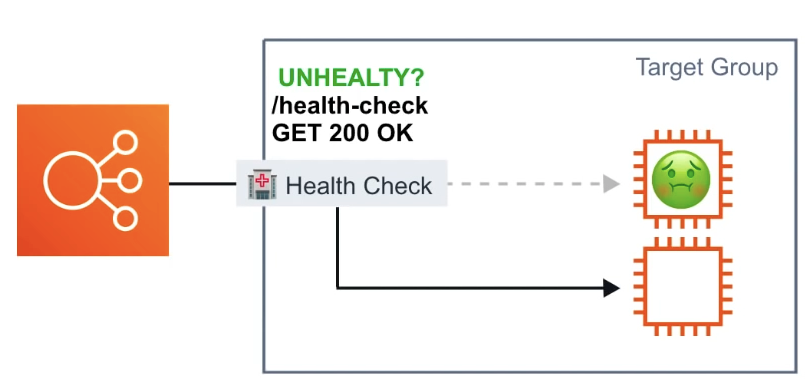
ALB and NLB HC are found on the target group
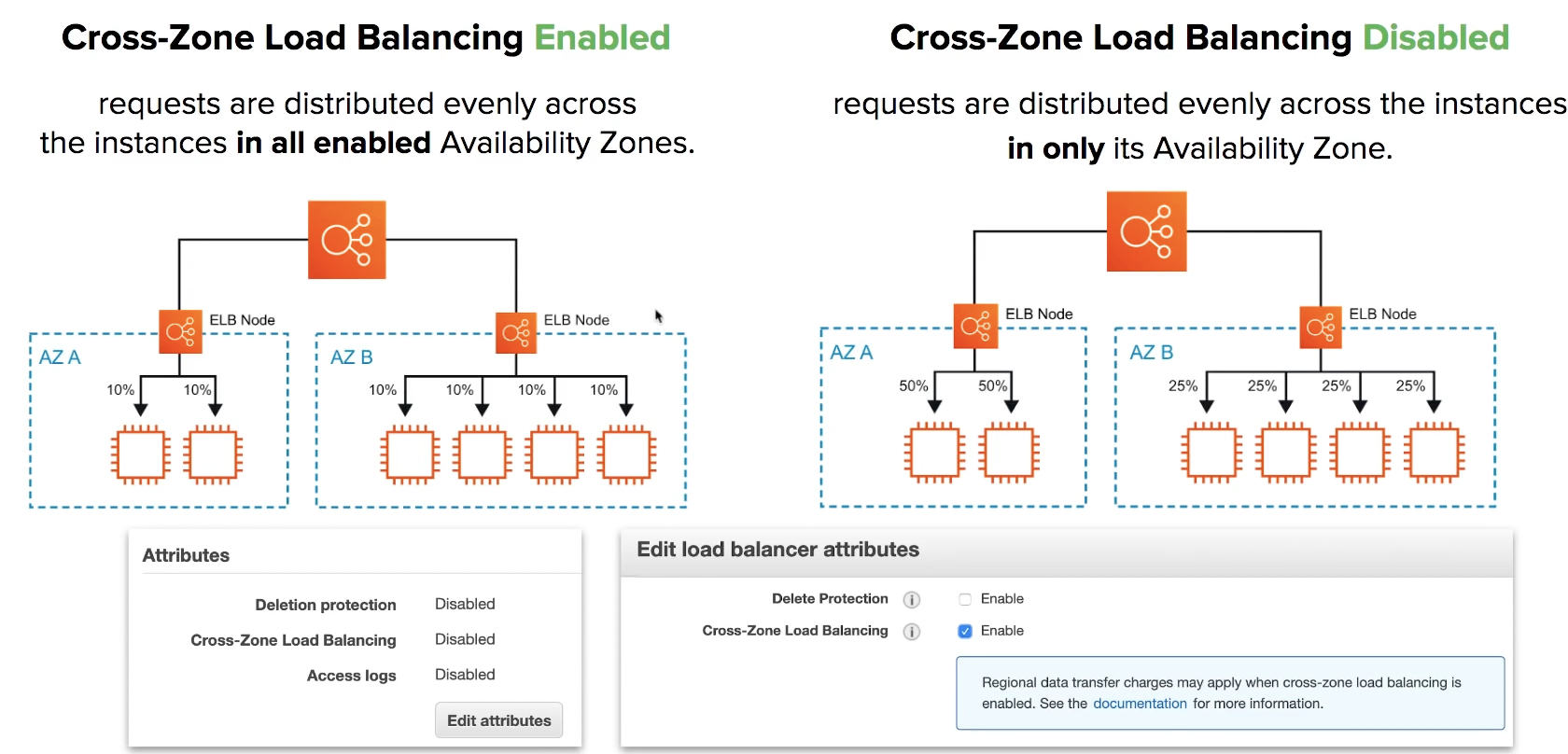
Cross-Zone Load Balancing
Only for CLB and NLB
Cross AZ
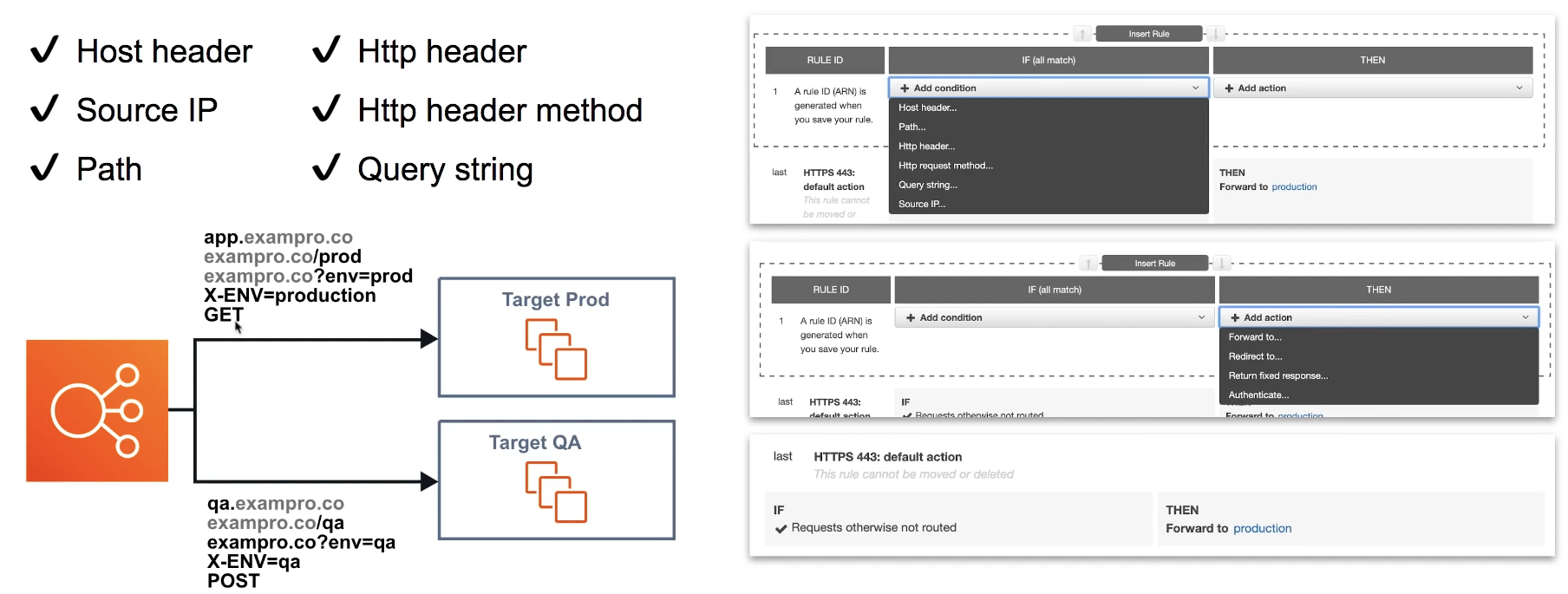
Requesting Routing
Apply rules to incoming request and then forward or redirect traffic
ELB Cheat Sheet
